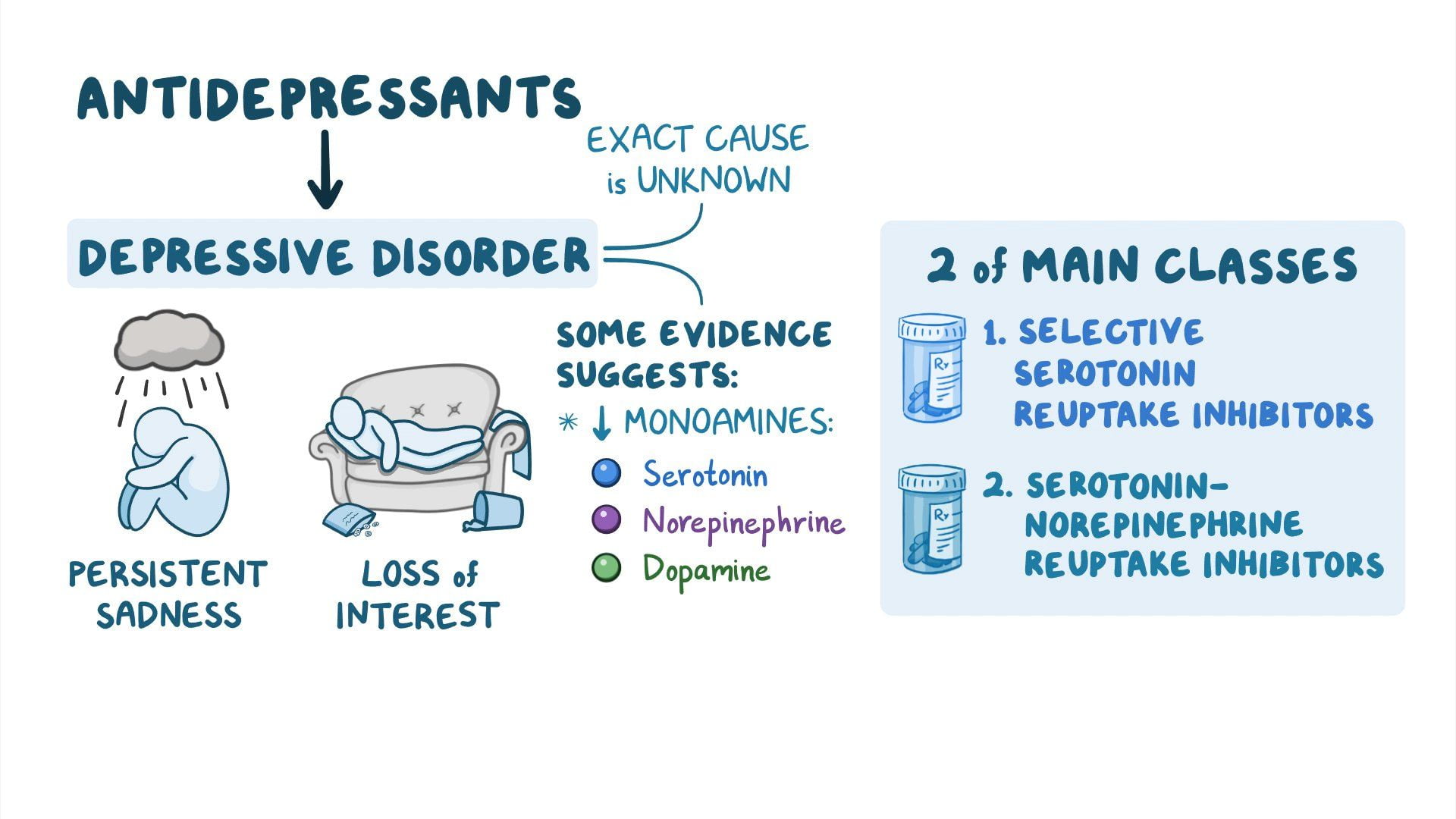
Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors (SSRIs) and Serotonin and Norepinephrine Reuptake Inhibitors (SNRIs) are two important classes of medicines that are prescribed to manage mental health conditions like depression and anxiety disorders.
Introduced in the 1980s and 90s, these medicines have revolutionized psychiatric treatment, providing increased safety, effectiveness, and tolerability from the previously available alternatives.
While both of these share common characteristics, several significant differences exist in how they function, their side effects, and overall efficacy, which makes it important to understand them before deciding between treatment options.
This blog provides an in-depth look at SSRI vs. SNRI, providing their importance, differences, similarities, and key details that every patient and prescriber should know.
SSRI vs. SNRI: Importance of Each Drug
Now that you know that the two classes of medicine have a significant role in tackling mental health conditions, what and how exactly do the two respond in functioning, and what needs to serve are the basic and important queries to be addressed.
The following section will elaborate on answering some similar queries and how evidential it is to use in critical health issues; let’s get started!
SSRI: Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors
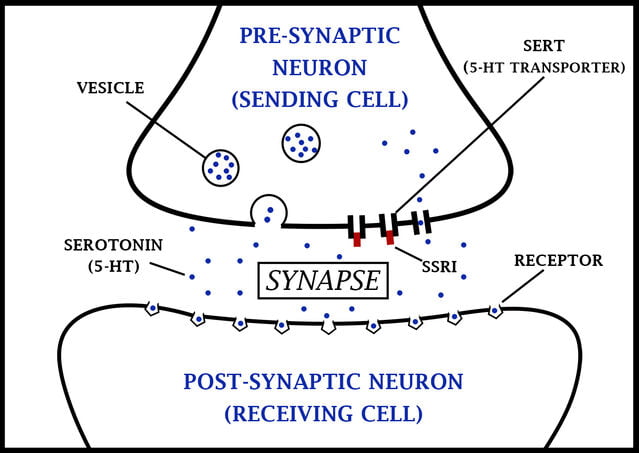
Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors have been a turning point in psychiatric treatment since their introduction in the 1980s. The development of SSRIs pushed forward a new era in treating mental health disorders, providing doctors with a significant tool and patients with a safe option to manage their conditions.
The key importance of SSRIs lies in the unique way they work. These block the reuptake of serotonin (as the name suggests), a neurotransmitter that is important in mood changes, social behavior, sleep, memory, and sexual functions—increasing the availability of serotonin in the brain—these help in improving the chemical imbalances that cause mental health disorders.
These are widely known for treating depression but are also used for the treatment of anxiety, panic, obsessive-compulsive, post-traumatic stress disorders, and other chronic pains.
Compared to older medicines, SSRIs have a lower risk of overdose and fewer side effects, thus making these a safer choice for patients.
SNRI: Serotonin and Norepinephrine Reuptake Inhibitors
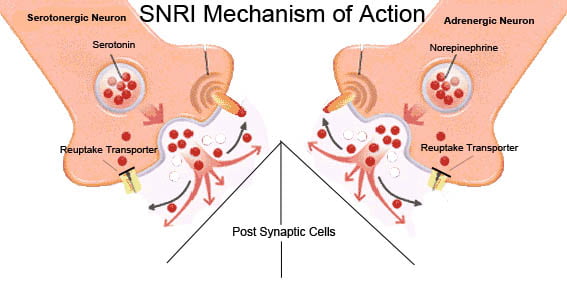
Serotonin and Norepinephrine Reuptake Inhibitors have marked essential progress in treating mental health disorders since they were released in the 1990s. Proceeding on the foundations laid by SSRIs, SNRIs have offered a broader spectrum of treatment options available for patients.
SNRIs work by blocking the uptakes not just of serotonin but norepinephrine as well. These increase two of the crucial neurotransmitters in the brain. Thus regulating mood, attention, and response actions. This dual action mechanism provides a broader therapeutic effect, making this potentially more effective for certain conditions that cannot be managed by SSRIs alone.
One of the major applications of SNRIs is the treatment of depression when SSRIs are ineffective. These are also helpful in managing various anxiety disorders, chronic neuropathic pain, fibromyalgia, and certain urinary incontinence.
This makes SNRIs critically important in clinical practice. Some common side effects include high blood pressure and sweating due to its impact on norepinephrine, but it provides an important alternative for people who do not respond to SSRIs.
‘SSRI vs. SNRI’: The Contentious Tussle
SSRI vs. SNRI is not about finding a winner but about understanding that these medicines provide various needs according to the individual needs, response to the treatment, and tolerability.
Both have been valuable in improving the patient’s quality of life, reducing the burden of mental health disorders, and effectively managing mental conditions.
Both represent significant progress in treating mental health disorders, offering targeted therapy options with less risk of overdose and side effects than earlier available medicines.
SSRI and SNRI: Understanding the Similarities
SSRI and SNRI are two major classes of medication used in treating various mental health conditions. When we discuss SSRI vs. SNRI, it is important to understand that these medications share multiple similarities despite being different in their mechanism of action.
SSRI and SNRI modulate neurotransmitter levels in the brain, the chemical messengers that transmit signals between nerve cells. While they have different targets – SSRIs focus on serotonin, and SNRIs target serotonin and norepinephrine. The objective of both is the same: treatment of neurotransmitter imbalances that lead to mental health disorders.
Another important similarity in the SSRI vs. SNRI comparison is the therapeutic use. Both classes are approved for a range of mental disorders, which include anxiety, panic, OCD, and major depressive disorders.
Additionally, both are effective in treating various types of chronic pain. Both are taken orally and prescribed once daily. It is also important to know that both share almost the same side effects, including nausea, sleep issues, and weight alterations.
Both SSRI and SNRI require careful discontinuation to prevent withdrawal syndrome, which is noticeable in the form of anxiety and nausea symptoms.
SSRI and SNRI: An Insight into the Difference in Detail

While both medicines are used in treating various mental health problems, it is essential to understand the differences between them while choosing the right treatment options. One of the major differences between them is the mechanism of how they work.
SSRIs inhibit the reuptake of serotonin and increase its availability in the brain. SNRI blocks the reuptake of both serotonin and norepinephrine, making it more effective against low energy or fatigue.
Both may have side effects such as nausea and sexual dysfunction, but SNRIs may lead to more side effects, such as blood pressure increase and sweating, due to the increase in norepinephrine. SSRIs may have problems with people who take other medications, thus making SNRIs a better option two for people who take multiple medicines.
The response to treatment also plays an important role in differentiating SSRI vs. SNRI . Some patients may feel better from an SSRI, while others may find more relief from certain SNRIs. Individual variability plays a critical factor in personalizing treatments.
Another important factor to consider is the cost of the two. Generic SSRIs are cheaper than SNRIs if the person is on long-term treatment.
Crucial Insights: Navigating SSRI vs SNRI
As we explore the topic of SSRI vs. SNRI more deeply, it is important to remember that these classes of medications play an important role in managing various mental disorders.
The effectiveness of both, however, varies with every individual, choosing between the two more of a personalized treatment instead of one fit-for-all option. Here are some important insights that can help you choose between the two.
1. Understanding Individual Needs

The choice between choosing an SSRI or an SNRI depends on the specific symptoms that a person is experiencing. SSRIs can be the first line of treatment because it has fewer side effects.
If the patient’s depression is described as fatigue, SNRI can be a better choice due to its dual action mechanism that affects both norepinephrine and serotonin.
Patients with existing conditions like chronic pain or fibromyalgia may also respond better to SNRIs. A person’s tolerance and lifestyle can affect the choice as well. The final goal is to find the treatment that aligns with the person’s unique needs for the best quality of life.
2. Patient History

Patient medical history gives an essential roadmap when choosing between SSRIs and SNRIs. Previous response to a particular class guides the choice of similar medications and increases the chances of successful treatment.
On the other hand, a history of reactions, tolerability problems, or non-response to a certain medicine class is just as important. This helps in suggesting an alternative medication class.
Past and present health issues also serve as an important factor, as some conditions may respond better to one the other. Each patient’s medical history is unique; thus, using it to choose a treatment offers benefits.
3. Side Effects

Considering SSRI vs. SNRI, it is important to understand the side effects of both. Both medicine classes can cause nausea, sleep disturbances, and sexual dysfunction.
Other than these common side effects, both have a few unique side effects as well. SNRIs, due to their effect on norepinephrine, can cause blood pressure spikes and even sweating.
SSRIs can interact with other medications, leading to careful monitoring of a person’s health. The important point is to balance the benefits of the medication with the side effects. Personal and medical situations can guide the process, increasing the benefits and minimizing the side effects.
4. Slow and Steady Approach
The most effective approaches in psychiatry are ‘slow and steady’ and adjustment when dealing with SSRIs and SNRIs. This approach starts with a low dose of the medication and then eventually increases the dosage as tolerated.
This helps reduce the potential side effects and allows the doctor to monitor the patient’s response to the medication.
It is also important to know that medications such as these antidepressants (SSRIs and SNRIs) take several weeks to reach their full effect. Thus, patience and regular contact with the doctor are important components of successful treatment.
5. Interdisciplinary Collaboration

This is the most important part of the management of mental health disorders. It usually takes a team of psychologists, psychiatrists, and other specialists to provide complete care.
While a psychiatrist may prescribe SSRIs or SNRIs and monitor the effects, a doctor can manage the overall health; a psychologist may be able to help with cognitive-behavioral therapy, etc.
This collaborative approach makes sure that all the patient’s conditions are addressed for effective care.
6. Ongoing Monitoring and Adjustment
For an SSRI and SNRI treatment to be successful, it is crucial that monitoring and adjustment of the medicines take place periodically. The process is not static and requires regular follow-ups and medication adjustments to check for side effects and response to the medicines. It is important for the doctor to closely monitor tolerability, overall patient health, and symptom improvement.
Adjustments may be required as the patient’s condition may change, new symptoms, old symptoms, or even overall health conditions. This ensures a dynamic treatment that changes according to the patient’s needs.
7. Managing Discontinuation

A careful and methodological approach is required to avoid withdrawal symptoms of SSRIs and SNRIs or relapse of the mental condition. These medicines should not be stopped without the guidance of a doctor or abruptly.
A gradual reduction in dosage or ‘tapering’ is recommended to allow the brain to adjust neurotransmitter changes. Symptoms of withdrawal may include mood swings, sleep issues, dizziness, and nausea.
Open communication with doctors, adherence to the advice given by them, and reporting new symptoms are important during the process.
Conclusion
The choice between SSRIs and SNRIs for treating mental health disorders is a patterned decision. While both have similar goals – to treat mental health symptoms by increasing the availability of neurotransmitters in the brain, the choice is not choosing a superior option in SSRI vs. SNRI but individualizing the treatment based on the patient’s requirements.
We believe that this detailed elaboration on the two will help you in making smart decisions about the choices that are individual to the choices of patients individually.
Suppose you or your loved one faces a problem while deciding on mental health. In that case, understanding these factors is pertinent and crucial in overcoming the menace at the earliest.
At the same time, it is essential to understand that counseling with a mental health professional to evaluate the symptoms and preferences is an unskippable next step.
Remember, whether it is choosing SSRIs or SNRIs, it is more than just a medication; it is about an approach that affects the person’s life as a whole.




