Many people turn to Bang energy drinks for a quick boost, believing they’re healthier than other options. However, the high caffeine content in these drinks may be cause for concern.
In this article, we’ll take an honest look at the caffeine in Bang and the potential risks it poses to your health.
By examining the ingredients and comparing the caffeine levels to recommended daily limits, we’ll help you understand the true nature of Bang energy drinks.
We’ll also explore the side effects of excessive caffeine intake and provide guidelines for consuming these beverages responsibly.
Join us as we uncover the facts about Bang’s caffeine content and what it means for your well-being.
The Caffeine Content in Bang Energy

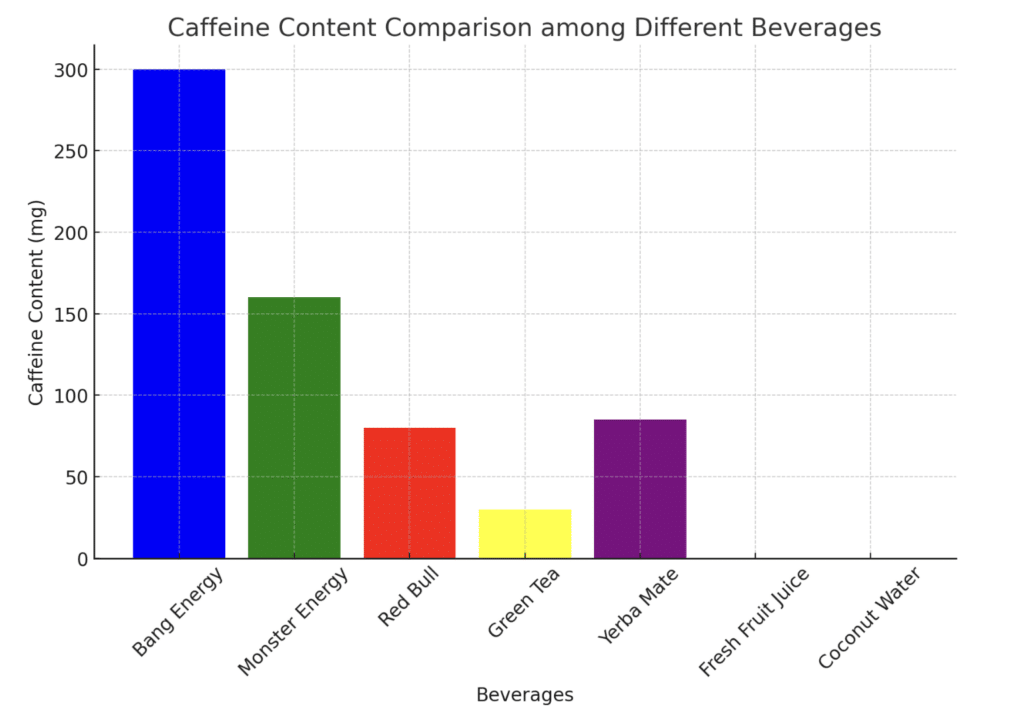
Each 16 fl oz can of Bang Energy contains 300 mg of caffeine, equivalent to about three cups of coffee. This is a significant amount of caffeine compared to other popular energy drinks and beverages.
Bang Energy- Nutritional Value
| Nutrient | Amount Per Serving (16 oz can) |
|---|---|
| Calories | 0 kcal |
| Total Fat | 0g |
| Saturated Fat | 0g |
| Trans Fat | 0g |
| Cholesterol | 0mg |
| Sodium | 40mg |
| Total Carbohydrates | 0g |
| Dietary Fiber | 0g |
| Total Sugars | 0g |
| Includes Added Sugars | 0g |
| Protein | 0g |
| Vitamin D | 0mcg |
| Calcium | 5mg |
| Iron | 0mg |
| Potassium | 85mg |
| Vitamin C | 27mg |
| Magnesium | 5mg |
| Niacin (Vitamin B3) | 5mg |
| Vitamin B6 | 0.5mg |
| Vitamin B12 | 1.5mcg |
Symptoms of Caffeine Toxicity
Consuming excessive amounts of caffeine, such as through multiple cans of Bang Energy, can lead to a condition known as caffeine toxicity.
This occurs when the body has ingested more caffeine than it can process, leading to a range of unpleasant and potentially dangerous symptoms.
1. Insomnia and Sleep Disturbances
One of the most common symptoms of caffeine toxicity is insomnia or difficulty sleeping.
Caffeine’s stimulant effects can interfere with the body’s natural sleep-wake cycle, making it challenging to fall or stay asleep.
This can result in restless nights, frequent awakenings, and poor sleep quality.
2. Digestive Issues
High caffeine intake can also cause various digestive problems. Caffeine stimulates the production of stomach acid, which can lead to heartburn, acid reflux, and general stomach discomfort.
In some cases, excessive caffeine consumption may even contribute to the development of stomach ulcers.
3. Muscle Breakdown
Caffeine toxicity can have detrimental effects on the musculoskeletal system.
In extreme cases, it can cause rhabdomyolysis, which involves the breakdown of muscle tissue.
This can lead to muscle weakness, pain, and even kidney damage as the byproducts of muscle breakdown flood the bloodstream.
4. Arrhythmias and Heart Palpitations
Excessive caffeine intake can overstimulate the cardiovascular system, leading to abnormal heart rhythms known as arrhythmias.
These can manifest as heart palpitations, where the heart feels racing, pounding, or fluttering. While often harmless, these sensations can be frightening and may indicate a more serious underlying heart condition in some cases.
Long-Term Health Risks
In addition to the immediate symptoms of caffeine toxicity, chronic high caffeine intake can contribute to the development of severe health problems over time.
1. Chronic Hypertension
Regular consumption of large amounts of caffeine can cause persistent elevations in blood pressure, leading to chronic hypertension. This condition puts extra strain on the heart and blood vessels, increasing the risk of heart attack, stroke, and kidney disease.
2. Increased Risk of Heart Disease
Long-term excessive caffeine intake may also increase the likelihood of developing heart disease.
The constant stimulation of the cardiovascular system can cause damage to the heart muscle and arteries, contributing to the buildup of fatty plaques and increasing the risk of coronary artery disease.
3. Potential for Addiction and Dependence
Caffeine is a psychoactive substance that can lead to addiction and dependence when consumed in high doses over an extended period.
Regular consumption of drinks like Bang Energy can develop tolerance, where the body requires increasing amounts of caffeine to achieve the desired effects.
Attempting to cut back or quit caffeine abruptly can trigger withdrawal symptoms such as headaches, fatigue, irritability, and difficulty concentrating, making it challenging to break the cycle of dependence.
To minimize the risk of these long-term health problems, it is crucial to consume caffeine in moderation and be mindful of the total daily intake from all sources, including energy drinks like Bang Energy.
Suppose you experience symptoms of caffeine toxicity or suspect that your caffeine consumption is negatively impacting your health.
In that case, consulting with a healthcare professional for guidance on cutting back and managing any potential withdrawal symptoms is essential.
Comparative Analysis with Other Caffeinated Beverages
| Brand | Product | Caffeine Content per Can |
|---|---|---|
| Bang Energy | Standard 16 oz | 300 mg |
| Red Bull | Standard 8.4 oz | 80 mg |
| Monster Energy | Standard 16 oz | 160 mg |
| Rockstar | Standard 16 oz | 160 mg |
| NOS | Standard 16 oz | 160 mg |
| 5-Hour Energy | Standard 2 oz shot | 200 mg |
| VPX Redline | Standard 8 oz | 316 mg |
| Celsius | Standard 12 oz | 200 mg |
| AMP | Standard 16 oz | 142 mg |
| Full Throttle | Standard 16 oz | 160 mg |
Bang Energy Main Ingredients

Bang Energy drinks contain several key ingredients contributing to their energy-boosting effects and unique flavor profile.
1. Caffeine
Caffeine is well-known for its ability to increase alertness, improve focus, and boost energy levels. It is a common ingredient in many energy drinks, and Bang contains a particularly high dose.
Caffeine also impacts metabolism, potentially aiding in weight management when consumed in moderation.
2. Super Creatine
‘Super Creatine’ is a unique form of creatine that Bang claims has better absorption and additional brain benefits than regular creatine. However, more research is needed to confirm these claims.
3. BCAAs
The specific BCAAs found in Bang Energy are leucine, isoleucine, and valine. These amino acids are essential for muscle growth, repair, and recovery, making them popular among athletes and fitness enthusiasts.
The exact concentrations of each BCAA in Bang have not been disclosed.
4. Sucralose
Sucralose and acesulfame potassium are artificial sweeteners used to enhance the flavor of Bang without adding calories or sugar.
While they are generally considered safe, some studies suggest potential health risks associated with their consumption, such as metabolic issues and changes in gut bacteria.
Common Marketing Claims by Bang Energy

1. Enhanced Physical Performance
Bang Energy often promotes itself as a drink that can boost physical performance, endurance, and strength. However, while caffeine may provide a temporary energy boost, the long-term effects on athletic performance are less clear.
2. Mental Clarity and Focus
The drink is also marketed as a cognitive enhancer, claiming to improve mental clarity, focus, and concentration.
While caffeine can indeed provide a short-term boost in alertness, the effects are not long-lasting and may be accompanied by a subsequent crash in energy levels.
3. Zero Calorie and Sugar-Free
Bang Energy heavily emphasizes its zero-calorie and sugar-free status as a selling point for health-conscious consumers. However, the drink still contains artificial sweeteners, which may have their potential health risks and drawbacks.
Consumers must approach these marketing claims critically and base their decisions on reliable scientific evidence rather than the advertising hype.
While Bang Energy may provide a temporary energy boost, it is not a substitute for a balanced diet, regular exercise, and healthy lifestyle habits in promoting overall physical and mental well-being.
How Much Caffeine is Too Much?

The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has established guidelines for safe caffeine consumption.
The FDA recommends that most healthy adults consume no more than 400 milligrams (mg) of caffeine daily, roughly equivalent to four or five cups of coffee.
However, it’s important to note that individual tolerance to caffeine varies, and some people may experience negative effects at lower doses.
Regarding specific demographics, the FDA advises that pregnant women limit their caffeine intake to 200 mg daily, about two cups of coffee.
Consuming high amounts of caffeine during pregnancy has been linked to an increased risk of miscarriage and low birth weight.
People with certain medical conditions, such as heart disease, high blood pressure, or anxiety disorders, should also be cautious about their caffeine consumption.
Caffeine can exacerbate these conditions and interact with certain medications, so it’s essential to consult with a healthcare provider to determine a safe level of intake.
Case Study: Excessive Consumption and Hospitalization
In one notable incident, a 26-year-old man was hospitalized after consuming four cans of Bang Energy within 6 hours.
He experienced symptoms such as chest pain, palpitations, and difficulty breathing. Upon examination, doctors found that he had an abnormally fast heart rate and elevated blood pressure.
The patient required medical intervention to stabilize his condition and was advised to avoid excessive caffeine consumption in the future.
This case highlights the importance of moderation when consuming high-caffeine energy drinks like Bang Energy.
Consuming multiple cans within a short timeframe can overwhelm the body’s ability to process caffeine, leading to potentially severe symptoms that may require medical attention.
Healthier Alternatives to Bang Energy
1. Natural Energy Boosters
- Green Tea: Rich in antioxidants and containing a moderate amount of caffeine, green tea can provide a gentle energy lift while offering potential benefits for weight management and heart health.
- Yerba Mate: This South American herbal tea is known for its energizing properties, thanks to its caffeine, theobromine, and theophylline content. It also contains various vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants.
- Coconut Water: A natural source of electrolytes, coconut water can help keep you hydrated and provide a natural energy boost without the added sugars or artificial ingredients in many energy drinks.
- Fresh Fruit Juices: Freshly squeezed or pressed fruit juices can provide a natural energy source through their natural sugars and a host of vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants.
2. Low-Caffeine Energy Drinks
For those who still prefer the convenience of energy drinks, options are available with lower caffeine content and more natural ingredients compared to Bang Energy.
- Guru Organic Energy: Made with organic ingredients and 100 mg of caffeine per can, Guru Organic Energy offers a more moderate caffeine boost and natural extracts like guarana and ginseng.
- Hiball Energy: With 100 mg of caffeine per can and no artificial sweeteners, Hiball Energy provides a cleaner energy drink alternative that is also low in calories.
The Controversy Surrounding Energy Drinks

The energy drink industry has faced significant controversy and regulatory scrutiny recently.
Many energy drink brands have been criticized for making unsubstantiated health claims, particularly regarding their ability to enhance physical and cognitive performance.
There have also been concerns about marketing these beverages to young consumers, with some brands using tactics such as social media influencers and sponsorship of extreme sports events to appeal to this demographic.
In response to these controversies, some countries have implemented regulations on the labeling and selling of energy drinks.
However, the regulatory landscape remains inconsistent, with different countries taking different approaches.
Conclusion
In conclusion, while Bang Energy may offer a quick energy boost and some potential nutritional benefits, it is crucial to be aware of the health risks associated with its high caffeine content.
Consuming excessive amounts of caffeine can lead to various short-term and long-term health problems, ranging from jitters and anxiety to chronic hypertension and heart disease.
To maintain overall well-being, it is essential to consume Bang Energy and other caffeinated beverages in moderation, if at all, and to prioritize obtaining nutrients from whole food sources.
If you are looking for healthier alternatives to boost your energy levels, consider trying natural options like green tea, yerba mate, or coconut water.
Remember, when it comes to your health, making informed decisions based on reliable information is always the best choice.
Frequently Asked Questions
What Would Happen if You Drank a Bang Everyday?
Drinking a Bang every day could lead to excessive caffeine intake, potentially causing anxiety, insomnia, digestive issues, and increased risk of heart problems over time.
What’s the Safest Energy Drink?
Energy drinks with lower caffeine content, natural ingredients, and no added sugars, such as Guru Organic Energy or Hiball Energy, are generally considered safer alternatives.
Is One Energy Drink a Day OK?
Consuming one energy drink daily is generally considered safe for most healthy adults. However, it’s important to be mindful of caffeine intake from other sources and individual tolerance levels. Moderation is key to minimizing potential health risks.




