In this blog post, we’ll take an in-depth look at Zevia, the popular zero-calorie soda, and examine its nutritional benefits.
We have thoroughly researched Zevia’s ingredients and their potential impact on your health.
By the end of this article, you will understand whether Zevia is a wise choice for your diet and lifestyle.
Let’s get started!
Overview of Zevia Products

Zevia is a brand that aims to provide healthier drink options than regular soda. It offers a variety of products, including sodas, energy drinks, teas, and mixers, catering to different tastes and preferences.
One of the key features of all Zevia products is that they are zero-calorie and sugar-free.
This makes them appealing to health-conscious consumers who want to enjoy a refreshing drink without the added sugar and calories found in traditional sodas.
Zevia- Product Range
| Product Type | Description | Available Flavors |
|---|---|---|
| Sodas | Zero-calorie, sugar-free sodas sweetened with stevia are available in various classic and unique flavors. | Black Cherry, Cola, Cream Soda, Ginger Ale, Grape, Orange, and many more. |
| Energy Drinks | Caffeinated beverages are designed to boost energy without added sugars and high calories. | Raspberry Lime, Mango Ginger, Kola, Grapefruit, Strawberry Kiwi. |
| Teas | Sugar-free teas from natural ingredients provide a refreshing and healthier alternative to sugary options. | Black Tea, Green Tea, Hibiscus Tea Passionfruit, Earl Grey Blood Orange. |
| Mixers | Specialty beverages are perfect for cocktails or alone, without artificial sweeteners. | Ginger Beer, Tonic Water, Lemon Lime with Bitters. |
Key Ingredients in Zevia
Zevia’s main ingredients are carbonated water, stevia leaf extract, natural flavors, and citric acid.
Carbonated water gives the drinks their signature fizz, while stevia leaf extract is a natural, zero-calorie sweetener. Natural flavors create various taste profiles, and citric acid is a preservative and flavor enhancer.
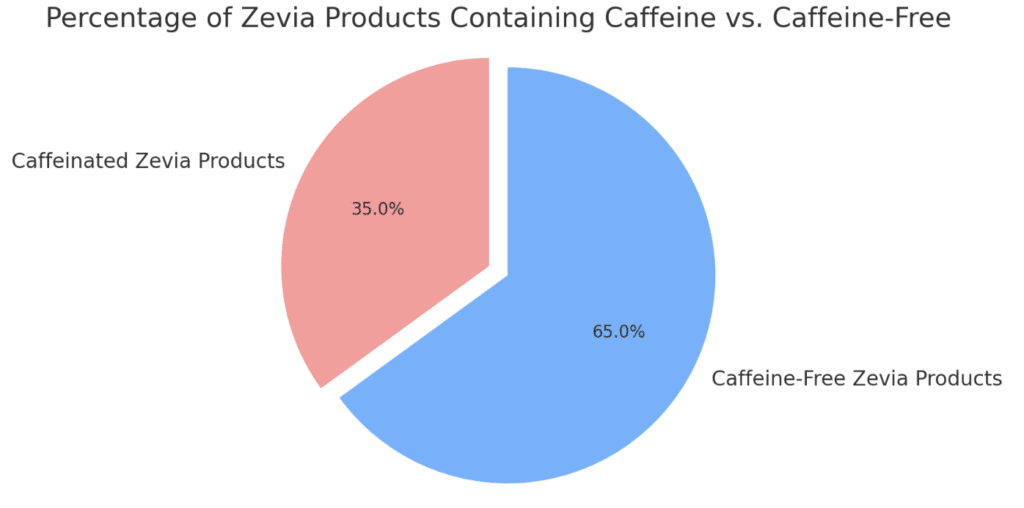
Some Zevia products contain additional ingredients like caffeine and organic teas. Caffeine is added to energy drinks and certain sodas to boost energy and alertness.
Organic teas, such as black, green, and hibiscus, are included in the tea line for their unique flavors and potential health benefits.
Nutritional Benefits
By avoiding refined sugar, Zevia can help reduce the risk of obesity, diabetes, heart disease, and other health issues associated with excessive sugar intake.
Stevia, the primary sweetener in Zevia, is a natural, low-calorie alternative to sugar that may offer anti-inflammatory properties and help regulate blood pressure.
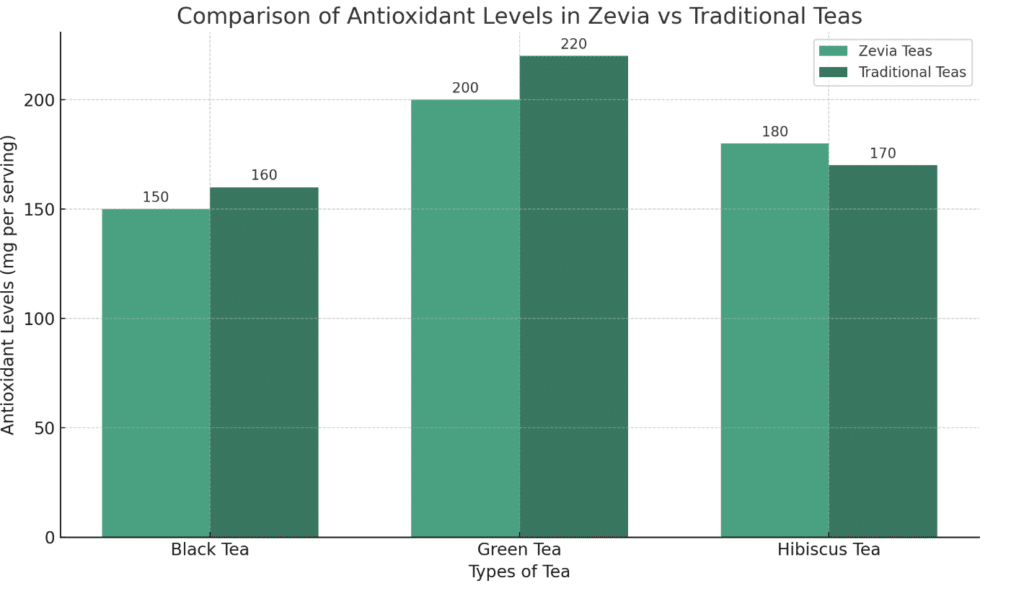
The organic teas used in some Zevia products can provide additional health benefits.
Black and green teas contain antioxidants that support heart health and may reduce the risk of certain cancers.
Hibiscus tea is known for its potential to lower blood pressure and support weight management.
Nutritional Concerns
| Ingredient | Found in Zevia | Potential Downsides | Common in Traditional Sodas | Potential Downsides |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stevia | Yes | It may affect the gut microbiome, causing potential sensitivity and digestive issues. | No | – |
| Citric Acid | Yes | It can contribute to dental erosion if consumed excessively. | Yes | It is the same as Zevia, plus the potential for stomach upset in sensitive individuals. |
| High Fructose Corn Syrup (HFCS) | No | – | Yes | Linked to obesity, diabetes, and metabolic syndrome, it can contribute to liver stress. |
| Aspartame | No | – | Often found in diet sodas. | Linked to controversy over potential neurological effects and metabolic concerns. |
| Phosphoric Acid | No | – | Yes | It can lead to bone density loss and dental erosion. |
While stevia is generally considered safe, some studies suggest it may negatively impact the gut microbiome, and certain individuals may be sensitive to it and experience digestive issues.
The use of natural flavors in Zevia products raises concerns due to the lack of transparency regarding their sources and potential health impacts.
The caffeine content in some Zevia drinks may concern children, pregnant women, and individuals sensitive to caffeine. Excessive caffeine intake can lead to jitters, anxiety, and sleep disturbances.
Comparative Analysis
| Attribute | Zevia | Traditional Sodas | Other Sugar-Free Beverages |
|---|---|---|---|
| Calorie Content | Zero calories | Typically, 100-150 calories per can | Varies, generally low to zero calories |
| Sugar Content | Sugar-free | High (often 20-40 grams per can) | Sugar-free or low-sugar |
| Type of Sweetener | Stevia (natural sweetener) | High fructose corn syrup or cane sugar | Artificial sweeteners (e.g., aspartame, sucralose) or other natural sweeteners (e.g., monk fruit) |
| Health Implications | Potentially beneficial for weight management, non-glycemic impact | Linked to obesity, diabetes, and other metabolic disorders | Varies; some artificial sweeteners are controversial regarding long-term health effects |
| Caffeine Content | Some varieties contain caffeine, comparable to other caffeinated sodas | Generally caffeinated except for specific ‘caffeine-free’ options | Varies; both caffeinated and caffeine-free options available |
| Flavor Variety | Wide range of flavors, including sodas, teas, energy drinks, and mixers | Wide range, primarily cola and fruit flavors | Wide range, including cola, fruit flavors, and more unique varieties |
| Additional Benefits | Vegan, non-GMO, no artificial colors or flavors | Often contains phosphoric acid, artificial colors, and flavors | Often contains preservatives and artificial flavors, though some are cleaner than others |
Consumer Guidance

In general, when consumed in moderation, Zevia can be a better choice than traditional sugary drinks.
However, it’s essential to consider individual health needs and sensitivities.
It’s best to opt for caffeine-free varieties or limit intake for those with caffeine sensitivity.
Individuals following strict sugar-free diets may find Zevia a suitable alternative, but it’s crucial to monitor the overall intake of sugar substitutes.
As with any food or beverage, moderation is key, and Zevia should be enjoyed as part of a balanced diet.
Conclusion
Zevia offers a range of zero-calorie, sugar-free beverages that can be a healthier alternative to traditional sodas.
By using natural sweeteners like stevia and avoiding refined sugar, Zevia can help reduce the risk of obesity, diabetes, and other health concerns.
However, it’s essential to be aware of potential downsides, such as the impact of stevia on gut health and the presence of citric acid and natural flavors.
When compared to other sugar-free beverages, Zevia stands out for its use of natural sweeteners, but moderation is still key.
As you consider your beverage choices, remember that while Zevia can be a better option than sugary drinks, it’s just one part of a balanced, healthy lifestyle.
So, what small change can you make today to improve your overall well-being?
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the Nutritional Value of Zevia Soda?
Zevia soda is sweetened with stevia and has zero calories, sugar, fat, protein, and total carbohydrates.
Why is Zevia Better Than Diet Coke?
Zevia is better than Diet Coke because it uses natural sweeteners and contains no artificial ingredients.
Does Zevia Spike Your Blood Sugar?
Zevia does not spike your blood sugar as it is sugar-free and uses stevia.
Is Zevia a Good Drink for Diabetics?
Zevia, being sugar-free with no impact on blood sugar levels, can be a good option for diabetics.
Is Zevia Safe to Drink Every Day?
Zevia is generally safe to drink daily if consumed in moderation. However, monitor any sensitivity to its ingredients like stevia or caffeine.




