Have you ever wondered if those crunchy shrimp tails are edible and good for you?
Many people believe that shrimp tails are just a garnish and should be discarded, but they may miss out on some surprising health benefits.
In this article, we’ll explore the nutritional value of shrimp tails and reveal whether they’re a healthy addition to your diet or a potential risk.
We’ll dive into the science behind the unique compounds found in shrimp tails, discuss how to prepare and eat them and address common concerns.
By the end, you’ll have a clear understanding of the pros and cons of eating shrimp tails and be able to make an informed decision about whether to include them in your meals.
Nutritional Content of Shrimp Tails
| Nutrient | Shrimp Tails |
|---|---|
| Protein (g) | 18.00 |
| Phosphorus(mg) | 201 |
| Fiber (g) | 1.20 |
| Calcium (mg) | 120.00 |
| Magnesium (mg) | 33.2 |
| Sodium (mg) | 94.4 |
| Iron (mg) | 0.433 |
| Zinc (mg) | 1.50 |
| Astaxanthin (mg) | 0.45 |
Comparative Nutritional Analysis
When compared to shrimp meat, the tails are notably richer in dietary fiber, particularly chitin, and contain higher levels of the antioxidant astaxanthin.
While the meat is an excellent source of lean protein and is low in fat, it may not provide the same fiber and antioxidant benefits as the tails.
By incorporating both the meat and the tails into your meals, you can take advantage of a wider array of nutrients.
This approach enhances the overall nutritional value of shrimp-based dishes, allowing you to enjoy the protein from the meat while also benefiting from the fiber and antioxidants in the tails.
Health Benefits of Eating Shrimp Tails
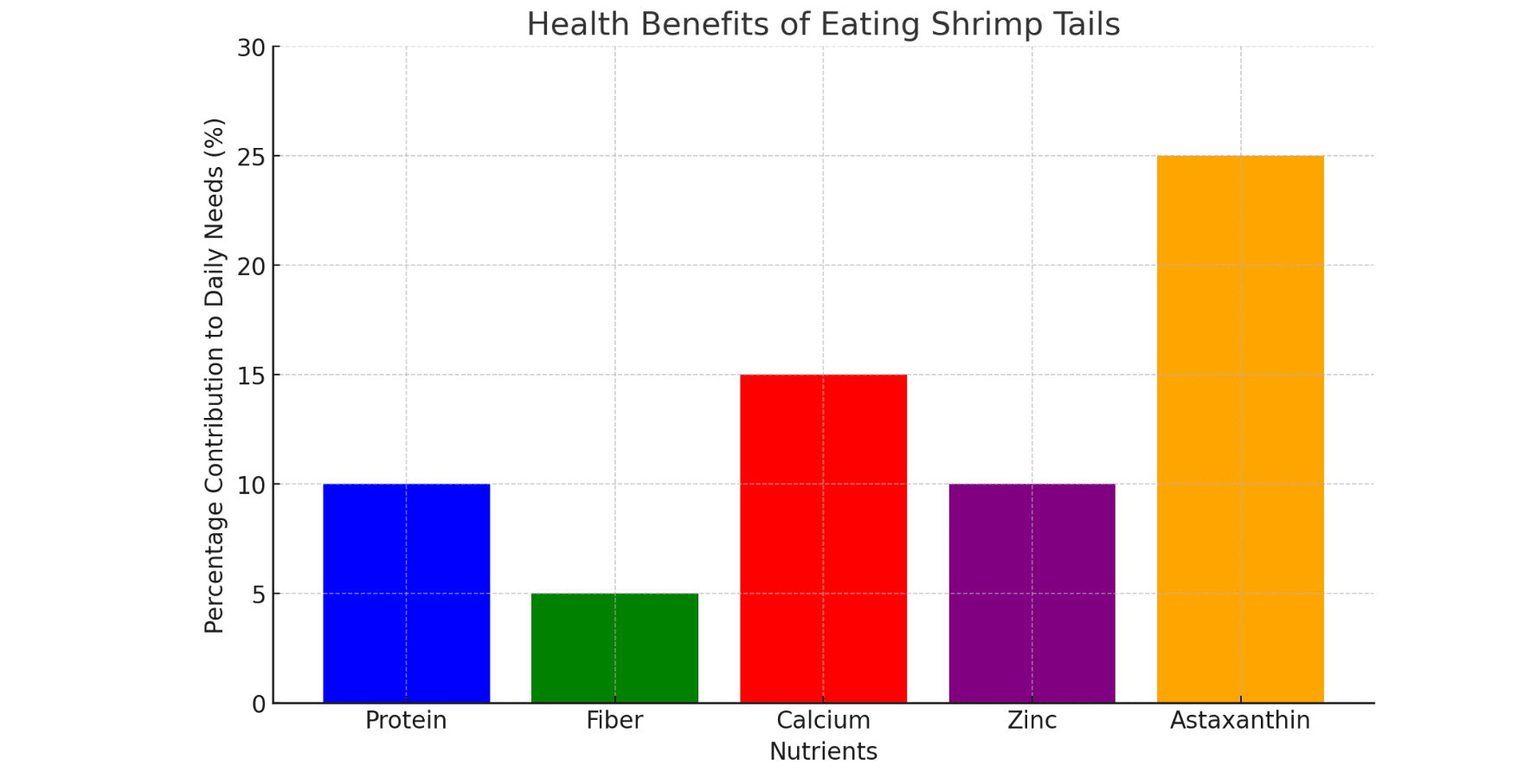
- Enhanced Digestive Health: The chitin found in shrimp tails acts as a dietary fiber that, while not digested by the body, plays a crucial role in supporting digestive health. Chitin helps promote regular bowel movements and aids overall digestion, keeping your digestive system running smoothly.
- Supports Weight Management: By incorporating the fiber-rich shrimp tails into your meals, you may experience a greater sense of fullness and satisfaction. This can lead to reduced calorie intake throughout the day, which benefits those looking to lose or maintain a healthy weight.
- Boosts Heart Health: Shrimp tails contain a powerful antioxidant called astaxanthin, which has been associated with improved heart health. Studies suggest that astaxanthin can help reduce inflammation in the body and may even contribute to lower blood pressure, both of which are important factors in maintaining a healthy heart.
- Improves Bone Strength: The trace minerals found in shrimp tails, such as calcium and zinc, are essential for building and maintaining strong bones. Regularly consuming shrimp tails as part of a balanced diet may help prevent bone loss and reduce the risk of conditions like osteoporosis.
- Enhances Immune Function: Zinc, one of the key minerals in shrimp tails, plays a vital role in supporting a healthy immune system. Adequate zinc intake helps your body fight off harmful pathogens and ensures that your immune response is functioning optimally.
- Anti-Aging Properties: The astaxanthin in shrimp tails is a potent antioxidant that helps combat free radicals in the body. Free radicals are known to contribute to the aging process and can cause damage to skin cells. By neutralizing these harmful compounds, astaxanthin may help improve skin health and reduce the visible signs of aging.
- Supports Eye Health: Astaxanthin has also been linked to better eye health, particularly in reducing the risk of age-related eye diseases like macular degeneration. Consuming shrimp tails regularly may help protect your eyes and maintain good vision as you age.
Culinary Uses of Shrimp Tails

Detailed Cooking Methods
- Grilling: Cooking shrimp with the tails on can add a smoky flavor and provide a convenient handle for easy eating. Marinate the shrimp for 15-30 minutes in a mixture of oil, citrus juice, and your favorite herbs or spices to achieve the best results. Grill the shrimp over medium-high heat for 2-3 minutes per side until they turn pink and the tails become crispy.
- Sautéing: Sautéing shrimp tails is a quick and flavorful cooking method. Heat a tablespoon of butter or oil in a skillet over medium-high heat. Add minced garlic and sauté until fragrant. Toss in the shrimp tails and cook for 3-4 minutes, stirring occasionally, until they turn pink and crisp up. Season with salt, pepper, and fresh herbs like parsley or cilantro for added flavor.
- Making Broths: Don’t discard your shrimp tails – they can be used to create rich and tasty seafood broths. In a large pot, sauté onions, carrots, and celery in a little oil until softened. Add the shrimp tails and any other seafood scraps you may have. Pour in enough water to cover the ingredients and bring to a boil. Reduce heat and simmer for 30-40 minutes, then strain the broth and use it as a base for soups, risottos, or sauces.
Enhancing Flavors and Textures in Dishes
Shrimp tails can impart a subtle seafood flavor to dishes without overwhelming them like whole shrimp.
They also add an interesting texture contrast in recipes like shrimp tempura, where the tails become crispy while the shrimp meat stays tender.
The crunchy tails in dishes like crispy shrimp tacos provide a pleasant counterpoint to the soft tortillas and toppings.
Incorporating shrimp tails can elevate a variety of dishes. In paellas or seafood stews, simmering the tails in the broth adds depth and complexity to the overall flavor profile.
Crispy fried shrimp tails make an attractive and tasty garnish for salads, kinds of pasta, or even as a topping for soups.
The possibilities are endless, and experimenting with shrimp tails can open up a new world of culinary delights.
Risks and Concerns

1. Digestibility and Dietary Concerns with Chitin:
Chitin, the fibrous substance that makes up shrimp tails, is not easily digestible by humans.
While it serves as a source of dietary fiber, which can benefit gut health, consuming large amounts of chitin or not preparing it properly may lead to digestive discomfort.
Individuals with sensitive digestive systems should be cautious when eating shrimp tails and consume them in moderation to avoid issues like bloating or stomach pain.
2. Potential Allergens and Safety of Consuming Shrimp Tails
Shrimp, including their tails, are a common allergen that can cause adverse reactions in some people.
Symptoms of a shellfish allergy may include hives, itching, swelling of the lips and tongue, difficulty breathing, and, in severe cases, anaphylaxis.
It’s crucial for individuals with known shellfish allergies to avoid consuming shrimp tails altogether.
Those unsure about their allergy status should consult with a healthcare provider before trying shrimp tails to ensure their safety.
3. Misconceptions About the Edibility and Taste of Shrimp Tails
There are some common misconceptions surrounding the edibility and taste of shrimp tails, which may discourage people from trying them.
Some believe that shrimp tails are inedible or have an unpleasant flavor. However, shrimp tails can be a delicious and nutritious addition to various dishes when prepared correctly.
Many cultures worldwide, particularly in Asia and Latin America, have long enjoyed the unique texture and taste of shrimp tails in their cuisine.
By dispelling these misconceptions and highlighting the culinary value of shrimp tails, more people may be willing to incorporate them into their diets.
Conclusion
Last but not least, shrimp tails offer a surprising array of nutritional benefits, from the digestive support of chitin to the heart-healthy and anti-aging properties of astaxanthin.
They can add unique flavors and textures to various dishes when prepared properly, elevating your culinary experience.
However, it’s essential to be mindful of potential risks, such as digestive discomfort for some individuals and the possibility of allergic reactions.
By consuming shrimp tails in moderation and staying informed about your health needs, you can safely incorporate this often-overlooked part of the shrimp into a balanced diet.
So, the next time you’re enjoying a shrimp dish, consider trying those crunchy tails – your taste buds and your body might just thank you for it!
Frequently Asked Questions
What Are the Pros and Cons of Eating Shrimp?
Pros: Nutritious, low in calories.
Cons: Potential allergen, high cholesterol, may contain contaminants.
Sustainable sources recommended.
Are Shrimp Tails Healthy?
Shrimp tails are edible and contain nutrients like calcium and fiber. However, they are tough and may pose a choking hazard. Eating them is a personal preference.
Why Do Fancy Restaurants Leave Tails on Shrimp?
Fancy restaurants leave tails on shrimp for presentation and as a handle for easy eating. It also shows the shrimp is whole and not a processed substitute.
Does the Shrimp Tail Have Cholesterol?
Yes, shrimp tails contain cholesterol, as do the rest of the shrimp. A 3-ounce serving of shrimp provides about 166 mg of cholesterol.




